Overview and principle of reciprocating vacuum pump
Date of issue:2021/8/19 15:31:09 Number of Views:
The limit vacuum of reciprocating vacuum pump (also known as piston vacuum pump) is 4 x 102pa -- 103pa in single stage, 1pA in two stages, and the pumping speed range is 45m3 / h-20000m3 / h. It is used to pump gas from sealed containers. The degree of extracted gas is not more than 35t. If auxiliary equipment such as freezer is added, it can also be pumped. The reciprocating vacuum pump has a large exhaust t capacity, which is mainly used for vacuum impregnation, vacuum treatment of molten steel, vacuum distillation, vacuum Yanfa, vacuum concentration, vacuum crystallization, vacuum dry bath, vacuum filtration and vacuum operation of concrete.
Reciprocating vacuum pump is not suitable for pumping corrosive gas or gas containing granular dust. If dust is contained in the pumped air, a filter must be installed at the inlet of the pump.
Since the piston ring and sealing ring of self-lubricating material are used in the oil-free reciprocating vacuum pump, there is no need to add oil for lubrication in the cylinder; An oil isolation chamber (its length is greater than a stroke length) is added between the cylinder and the engine body to prevent the lubricating oil in the engine body from leaking into the cylinder along the piston rod, so the pump has no pollution to the pumped system. Oil free reciprocating vacuum pump has vertical and horizontal structures.
The application scope of the pump is:
① In an environment requiring vacuum cleaning;
② When the gas is to be recovered, the inflation chamber can be filled with recovered gas to ensure the purity of the gas;
③ When the flammable and explosive gas is removed, the isolation chamber can be filled with inert gas, so that the air (suspect aid) cannot leak into the cylinder to avoid accidents.
Principle of reciprocating vacuum pump:
The working principle of reciprocating vacuum pump is shown in the figure. The main components are cylinder 1 and piston 2 in which reciprocating linear motion is performed. The piston is driven by crank connecting rod 3. In addition to the above main components, there are exhaust valve 4 and suction valve 5.
During operation, driven by the motor, the piston in the cylinder moves back and forth through the action of the crank connecting rod mechanism. When the piston moves from the left end to the right end in the cylinder, due to the increasing volume of the left chamber of the cylinder, the density of the gas in the cylinder decreases, forming an air extraction process. At this time, the gas in the container enters the left chamber of the pump body through the suction valve 5. When the piston reaches the rightmost position, the cylinder is completely filled with gas. Then, the piston moves from the right end to the left end, and suction valve 5 is closed. The gas in the cylinder is gradually compressed as the piston moves from right to left. When the pressure of the gas in the cylinder reaches or is slightly greater than the atmospheric pressure, the exhaust valve 4 is opened to discharge the gas into the atmosphere to complete a working cycle. When the piston moves from left to right again, it sucks in part of the gas and repeats the previous cycle. Until a stable equilibrium pressure is reached in the pumped container.
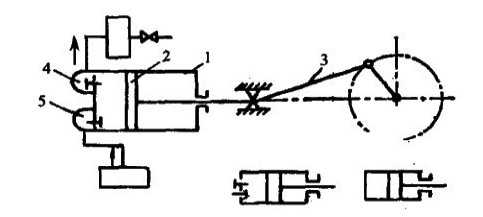
Fig. 3-1 working principle of reciprocating pump L - cylinder;
2 - piston;
3. Crank connecting rod mechanism;
4 exhaust valve;
5 - inspiratory reading
The limit vacuum of reciprocating vacuum pump (also known as piston vacuum pump) is 4 x 102pa -- 103pa in single stage, 1pA in two stages, and the pumping speed range is 45m3 / h-20000m3 / h. It is used to pump gas from sealed containers. The degree of extracted gas is not more than 35t. If auxiliary equipment such as freezer is added, it can also be pumped. The reciprocating vacuum pump has a large exhaust t capacity, which is mainly used for vacuum impregnation, vacuum treatment of molten steel, vacuum distillation, vacuum Yanfa, vacuum concentration, vacuum crystallization, vacuum dry bath, vacuum filtration and vacuum operation of concrete.
Reciprocating vacuum pump is not suitable for pumping corrosive gas or gas containing granular dust. If dust is contained in the pumped air, a filter must be installed at the inlet of the pump.
Since the piston ring and sealing ring of self-lubricating material are used in the oil-free reciprocating vacuum pump, there is no need to add oil for lubrication in the cylinder; An oil isolation chamber (its length is greater than a stroke length) is added between the cylinder and the engine body to prevent the lubricating oil in the engine body from leaking into the cylinder along the piston rod, so the pump has no pollution to the pumped system. Oil free reciprocating vacuum pump has vertical and horizontal structures.
The application scope of the pump is:
① In an environment requiring vacuum cleaning;
② When the gas is to be recovered, the inflation chamber can be filled with recovered gas to ensure the purity of the gas;
③ When the flammable and explosive gas is removed, the isolation chamber can be filled with inert gas, so that the air (suspect aid) cannot leak into the cylinder to avoid accidents.
Principle of reciprocating vacuum pump:
The working principle of reciprocating vacuum pump is shown in the figure. The main components are cylinder 1 and piston 2 in which reciprocating linear motion is performed. The piston is driven by crank connecting rod 3. In addition to the above main components, there are exhaust valve 4 and suction valve 5.
During operation, driven by the motor, the piston in the cylinder moves back and forth through the action of the crank connecting rod mechanism. When the piston moves from the left end to the right end in the cylinder, due to the increasing volume of the left chamber of the cylinder, the density of the gas in the cylinder decreases, forming an air extraction process. At this time, the gas in the container enters the left chamber of the pump body through the suction valve 5. When the piston reaches the rightmost position, the cylinder is completely filled with gas. Then, the piston moves from the right end to the left end, and suction valve 5 is closed. The gas in the cylinder is gradually compressed as the piston moves from right to left. When the pressure of the gas in the cylinder reaches or is slightly greater than the atmospheric pressure, the exhaust valve 4 is opened to discharge the gas into the atmosphere to complete a working cycle. When the piston moves from left to right again, it sucks in part of the gas and repeats the previous cycle. Until a stable equilibrium pressure is reached in the pumped container.

Fig. 3-1 working principle of reciprocating pump L - cylinder;
2 - piston;
3. Crank connecting rod mechanism;
4 exhaust valve;
5 - inspiratory reading